Historical Articles
This page contains my historical articles about machine learning and cognitive computing. These are older posts that have been moved to this archive section.
-
Amazon SageMaker con Microsoft CNTK/Keras
January, 2018

I marchi sono di proprietà dei legittimi proprietari. SageMaker è l'ambiente di Amazon che facilita la costruzione e distribuzione di modelli Machine/Deep Learning. Sostanzialmente è un servizio gestito della piattaforma AWS che agevola l'adozione di un paradigma di design & deploy basato su containerizzazione Docker, packaging di web service su lightweight serving stack come Nginx + Gunicorn + Flask e diverse altre amenità.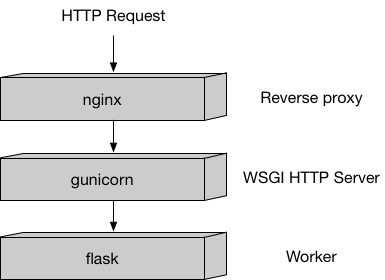
Serving stack utilizzato in SageMaker. Nginx è il server HTTP e reverse proxy, open source e ad alte prestazioni, noto per le sue elevate prestazioni, stabilità, ricco set di funzioni, semplicità di configurazione e basso consumo di risorse. Nginx assolve il ruolo di server di buffering di interfaccia. Green Unicorn (gunicorn) è un server HTTP/WSGI (porting del progetto Ruby Unicorn) con bilanciamento del carico tramite pre-fork e socket condivisi. Flask è un framework scritto in Python, basato su librerie altamente performanti per la gestione del protocollo WSGI e il templating. -
Intuitions on the fly on Blockchain
May, 2017

Image source: Icons8. Distributed under Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported. An increasing number of articles suggest fascinating combinations of Blockchain and Machine Learning. It could be useful to introduce some intuitions about what is a blockchain, before venturing forth.In the 2008 Bitcoin entered the market. It was a pioneering payment method and cryptocurrency.
The technology underlying Bitcoin is called Blockchain. Nowadays Bitcoin is the most important implementation of Blockchain. However, in the last 2 years many opportunities have emerged and Blockchain has assumed a central role in different contexts.
It is not simple to exactly explain how Blockchain works because it is a combination of different technologies. More appropriately, Blockchain is an ecosystem where different technologies, approaches and theories converge.
-
Hype cycle e Apprendimento Automatico: in che fase siamo?
April, 2017
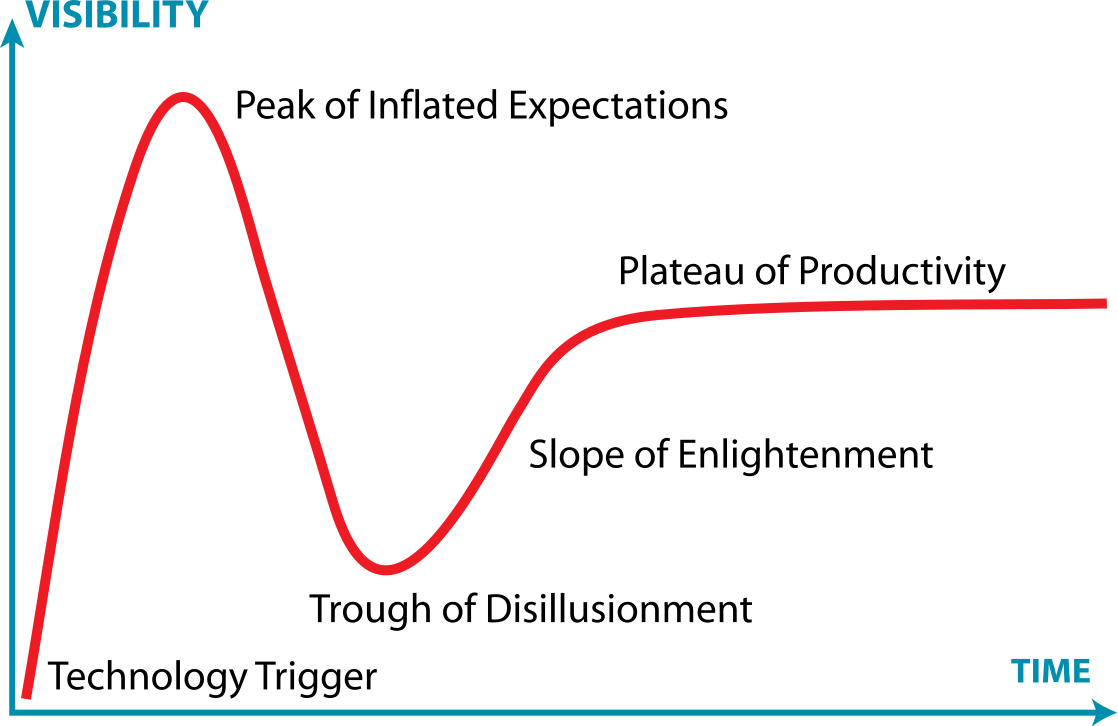
Image source: Wikimedia. Distributed under GNU Free Documentation License Ogni trend tecnologico si sviluppa attraverso una successione di fasi che ne caratterizza il processo di maturazione: dall'emersione alla sua accettazione. Tale processo è sempre accompagnato da un "buzzing tecnologico" che solitamente esplode nelle fasi iniziali di maggiore "illusione" per poi rimodularsi progressivamente in funzione dell'accettazione da parte del pubblico. Semplificando, il ben noto hype cycle (ciclo dell'esagerazione) di Gartner potrebbe essere considerato come una metodologia che ci aiuta a riassumere graficamente lo stato del buzzing che avvolge una grande varietà di trend tecnologici. -
Emotions Detection Via Facial Expressions with python & OpenCV
January, 2017
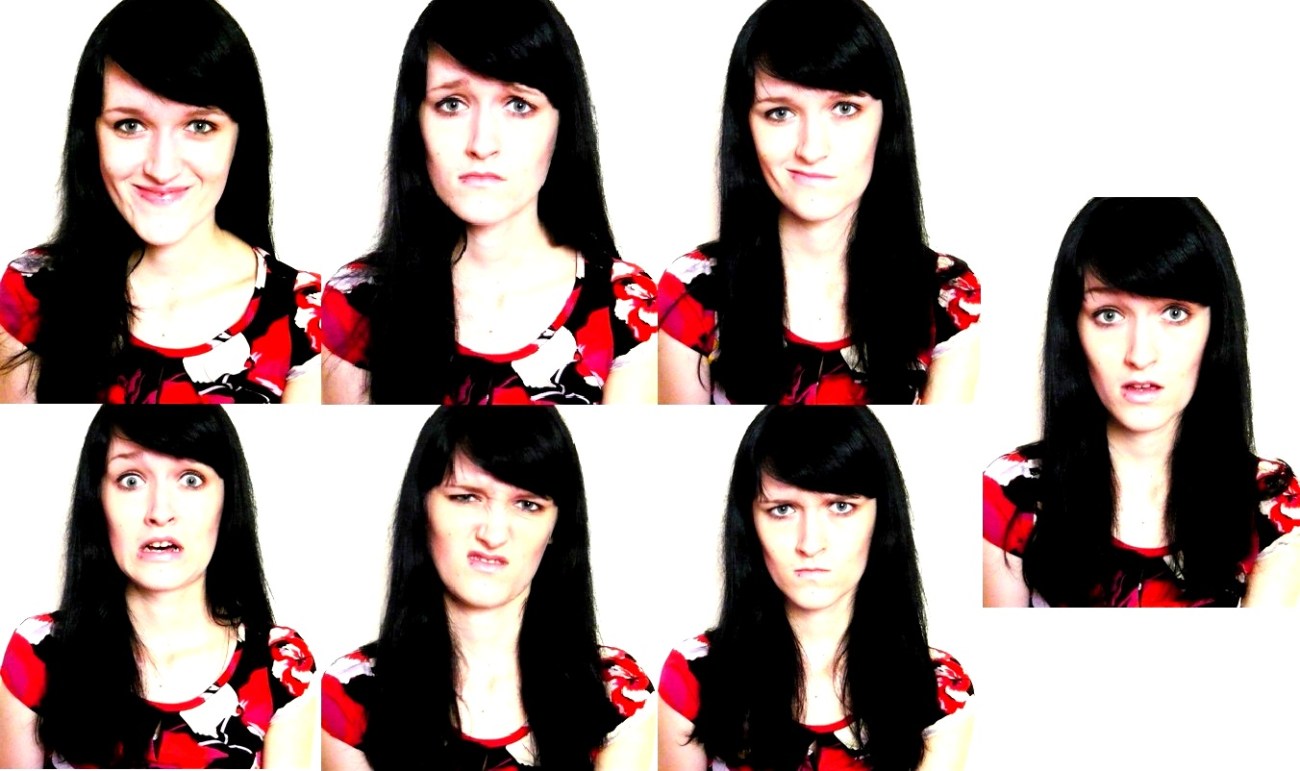

In this tutorial I aim to quench a subset of your machine learning thirst; And for what other reason would you be here? This tutorial is based on training a computer to recognize not just your face but the emotion expressed on it. How cool is that? Imagine walking into your home after a long day of work, and your computer immediately knows what kind of therapeutic music to play based on how you are feeling, or when you are driving the car onboard computer is able to assess your ability to drive based on your emotions. -
Introduction to gradient-boosted trees and XGBoost hyperparameters tuning (with python)
January, 2017
XGBoost model is a supervised machine learning algorithm that takes in the training data and constructs a model that predicts the outcome of new data instances.XGBoost has gained a lot of popularity in the machine learning community due to its ability to train versatile model with speed and quality performance. It's an implementation of gradient boosted decision trees which are constructed for speed and performance.
For an in-depth introduction visit this link for more technical details.
Here we cover a gentle introduction of XGBoost model using python scikit-learn package.
By the end of this tutorial you will have learnt:
XGBoost installation for python use
XGBoost data preparation and model training
XGBoost model prediction
XGBoost hyperparameters tuning
-
Introduction to decision trees with BigML: a step by step guide
December, 2016
The discussion on machine learning is the buzz word in the current tech tectonic waves. It's all amber-hot as the machines are nearly on the verge of learning to do things and react to the environment around them in more human-like-unsupervised-design.Machine learning is a field of neuro-computational studies, in which scientists work towards instilling learning capabilities in a computer memory. This is all possible through implementation of a set of supervised or unsupervised rules referred to as algorithms. The most popular machine learning algorithms are artificial neural networks, support vector machines, k-nearest neighbors and decision trees. We will discuss the decision trees in this context.
-
Machine Learning: the best cheat sheets in one page
December, 2016

Squeezed into a set of short tips and schemes, a cheat sheet is not only a source for visual inspiration but also a quick way to learn something new, as well as to refresh your knowledge about any particular subject. -
Understanding Apache Ecosystem: stream processing
November, 2016

In this article I will show how a normal big data/machine learning project progresses, taking in account the stream processing and analysis part. I will try to functionally position a wide variety of Apache projects such as Sqoop, Flume, Kafka, Hadoop, Storm, Spark, Samza, Flink, Beam, Oozie, Thrift. -
A gentle introduction to TensorFlow with python (and RNN)
November, 2016

My quick and dirty introduction to TensorFlow. -
Riconoscimento vocale e analisi di testo non strutturato con Watson Developer Cloud Python SDK
November, 2016
In questo post illustro come: estrarre tracce audio da filmati (usando, per esempio, YouTube), eseguire una conversione del parlato in testo (speech to text), estrarre conoscenza dal testo non strutturato della trascrizione. -
Image recognition tutorial in Python/MXNet using deep convolutional
October, 2016
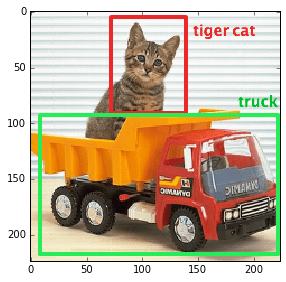
I would like to introduce in this post some specific CNN implementations which are able to offer a cognitive image processing that is very close to the state of the art. The exemplary code is based on the use of MXNet framework combined with the Python language.MXNet is an open source project, distributed under the Apache License Version 2.0, a result of the research and development groups' collaboration, belonging to important institutions such as CMU, NYU, NUS and MIT. It is a DMLC project. DMLC is a group of companies, laboratories and universities engaged in projects which are contributing from many years in defining the leading edge in the field of machine learning.
-
Exploring Tweets: a python-based demonstrator
August, 2016
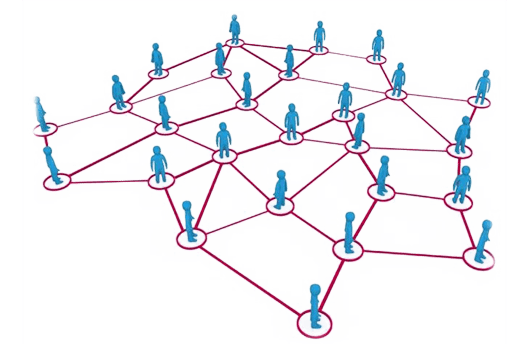
Tools based on visual representations of social networks are important to understand network data and convey the result of the analysis. Visualization facilitates qualitative interpretation of network data. This kind of tools helps us to identify key influencers, contents, and to focalize attention on interesting users optimizing our time. -
Identificazione di oggetti in immagini con Convolutional Neural Network, Python e MXNet
August, 2016

Ci sono molti strumenti che permettono di identificare un oggetto in un'immagine, come ad esempio il modello bag of visual words, tramite i descrittori di feature SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) o SURF (speeded up robust feature), oppure l'utilizzo delle macchine a vettori di supporto (SVM, support vector machine); tuttavia, in questi ultimi anni, le reti neurali profonde (DNN, deep neural networks) hanno contribuito con un nuovo impulso alla ricerca e sono, pertanto, sempre più utilizzate. Infatti, l'abilità delle DNN nell'apprendere, a partire da grandi insiemi di esempi, funzioni complesse, non-lineari e ad alta dimensionalità, le rende perfette candidate per i compiti di riconoscimento di immagini. Un tipo particolare di DNN sono le reti neurali convoluzionali (CNN, convolutional neural networks) usate con grande successo per problemi di riconoscimento automatico di pattern bidimensionali come la rivelazione di oggetti, facce e loghi nelle immagini. In questo post introduco alcune specifiche implementazioni di CNN in grado di offrire un'elaborazione cognitiva delle immagini che è molto prossima allo stato dell'arte. Il codice esemplificativo è basato sull'impiego del framework MXNet in combinazione con il linguaggio Python.